Structure And Chemical Formula
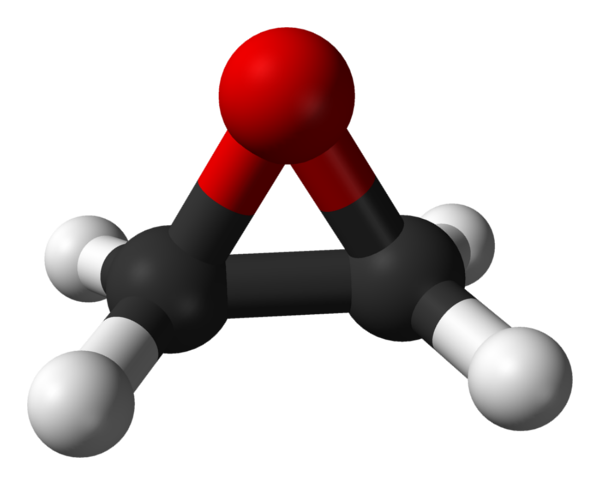
The epoxy cycle of ethylene oxide is an almost regular triangle with bond angles of about 60 degree and a significant angular strain corresponding to the energy of 105 kJ/mol. For comparison, in alcohols the COH angle is about 110 degree; in ethers, the COC angle is 120 degree. The moment of inertia about each of the principal axes are IA = 32,921.^-40 g.cm2, IB = 37,926.10^-40 g.cm2 and IC = 59,510.10^-40 g.cm2. The relative instability of the carbon-oxygen bonds in the molecule is revealed by the comparison in the table of the energy required to break two CO bonds in the ethylene oxide or one CO bond in ethanol and dimethyl ether.
C2H4O