
Ethylene oxide is an industrial chemical that typifies the dilemma that the world faces today. It has proven very valuable in the formulation and manufacture of many types of products. An entire industry has grown up around its production and use. And it has serious human health and environmental effects.
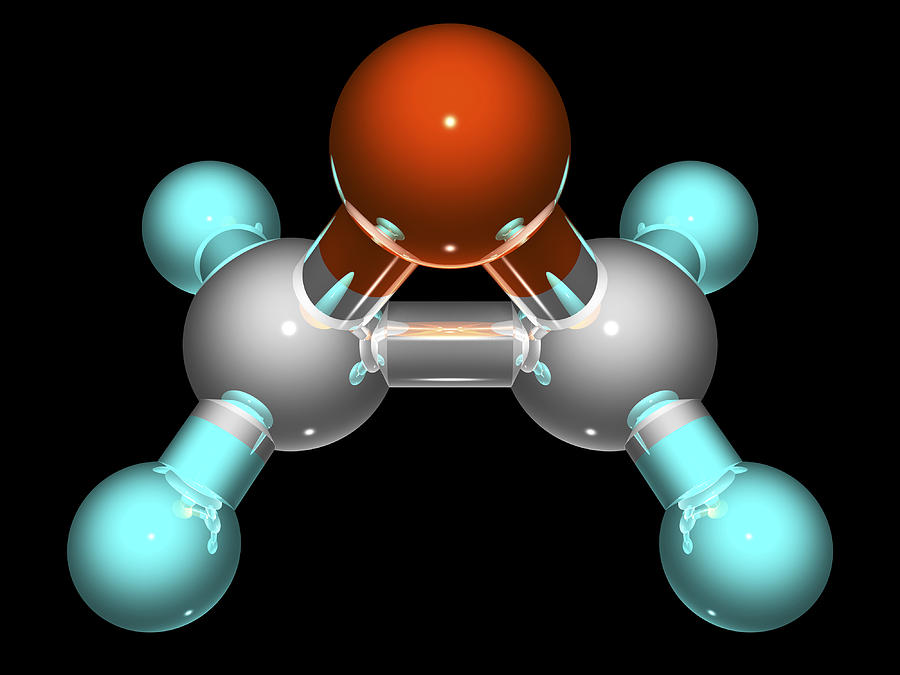
Ethylene oxide is one of the most important derivatives of ethene, and is produced from the reaction between ethene and oxygen through a catalytic oxidation process. Shown in the diagram below, its chemical formula is C2H4O. Due to its unique molecular structure it has become one of the principal raw materials used in the chemical and petrochemical industries. Ethylene oxide is a highly volatile, flammable gas with a somewhat sweet odour. It dissolves easily in water, alcohol and most organic solvents.
When ethylene oxide gas is produced or used, some of it is released to air and water. If it is released into the air, humidity and sunlight cause it to break down within a few days. In water, ethylene oxide will either break down or be destroyed by bacteria within a few days.
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set a limit of 1 ppm of exposure over an 8-hour workday, 40-hour workweek. The U.S. National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends that average workplace air should contain less than 0.1 ppm ethylene oxide averaged over a 10-hour workday, 40-hour workweek.