Definition of Paraben
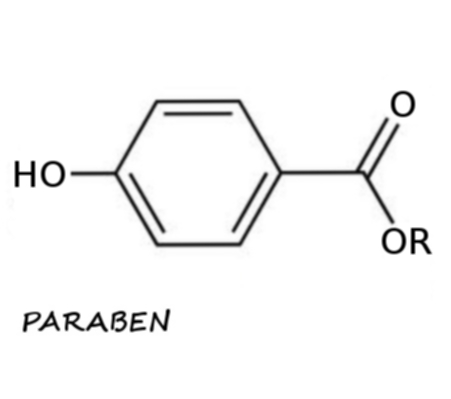
Parabens are a class of widely used preservatives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Chemically, they are a series of parahydroxybenzoates or esters of parahydroxybenzoic acid (also known as 4-hydroxybenzoic acid). Parabens are effective preservatives in many types of formulas. These compounds, and their salts, are used primarily for their bactericidal and fungicidal properties. They are found in shampoos, commercial moisturizers, shaving gels, personal lubricants, topical/parenteral pharmaceuticals, spray tanning solution, makeup, and toothpaste. They are also used as food additives. Their efficacy as preservatives, in combination with their low cost, the long history of their use, and the inefficacy of some natural alternatives like grapefruit seed extract (GSE), probably explains why parabens are so commonplace. No effective direct links between parabens and cancer have been established.
Definition of Methyl Paraben
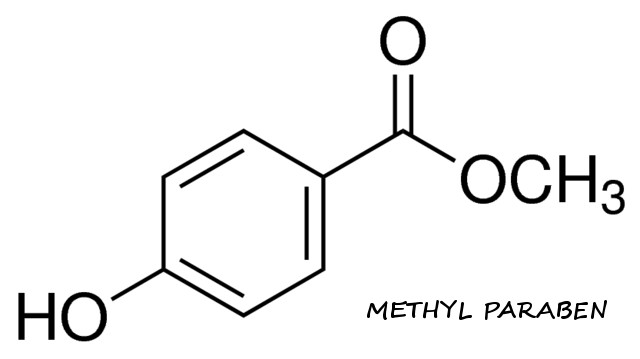
Methylparaben, also methyl paraben, one of the parabens, is a preservative with the chemical formula CH3(C6H4(OH)COO). It is the methyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Typically, this chemical will be formulated into creams and serums with other parabens, like butylparaben and propylparaben, though in some cases it may be used on a standalone basis. The goal of methylparabens and similar chemicals is to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungus. By limiting the growth of microorganisms, this ingredient helps preserve the integrity of skin care formulations for a longer period of time, and also protects the consumer from inadvertently adding contaminated products to their skin.