Definition of Cinnamaldehyde:
Cinnamaldehyde is the aldehyde that gives cinnamon its flavor and odor. Cinnamaldehyde occurs naturally in the bark of cinnamon trees and other species of the genus Cinnamomum like camphor and cassia. Cinnamaldehyde is also known as a corrosion inhibitor for steel and other ferrous alloys in corrosive fluids. It can be used in combination with additional components such as dispersing agents, solvents and other surfactants.
Structure Formula:
*2 Dimention.
*3 Dimention.
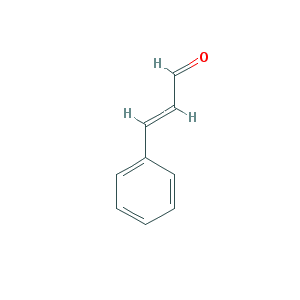
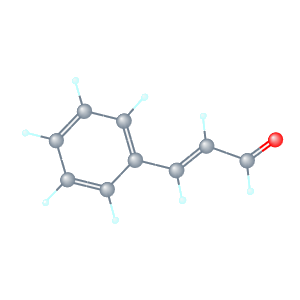
Preferred IUPAC Name: (2E)-3-Phenylprop-2-enal.
Other names:*Cinnamaldehyde
*Cinnamic aldehyde.
*trans-Cinnamaldehyde.
Chemical Formula: C9H8O
Linear Formula: C6H5CH=CHCHO
Appearance: Yellow oil

Molar Mass: 132.16 g/mol.
Density: 1.0497 g/mL.
Melting Point: -7.5oC (18.5oF; 265.6K.
Boiling Point: 248oC (478oF; 521K)
Solubility in water: Slightly soluble.
Solubility: *Soluble in ether, chloroform.
*Insoluble in petroleum ether.
*Miscible with alcohols, oil.
Magnetic Susceptibility: -74.8 x 10-6 cm3/mol.